Flesh Eating Bacteria in Florida: A Hidden Danger
Introduction
Florida, known for its stunning beaches and warm climate, is a prime tourist destination for many. However, beneath the picturesque landscapes lies a hidden danger – the dreaded “flesh-eating bacteria.” In this article, we will delve into the concerning issue of flesh-eating bacteria in Florida, exploring its causes, symptoms, prevention, and treatment. Join us on this informative journey as we uncover the facts about this potentially life-threatening threat lurking in the Sunshine State.
What is Flesh-Eating Bacteria?
A Silent Threat
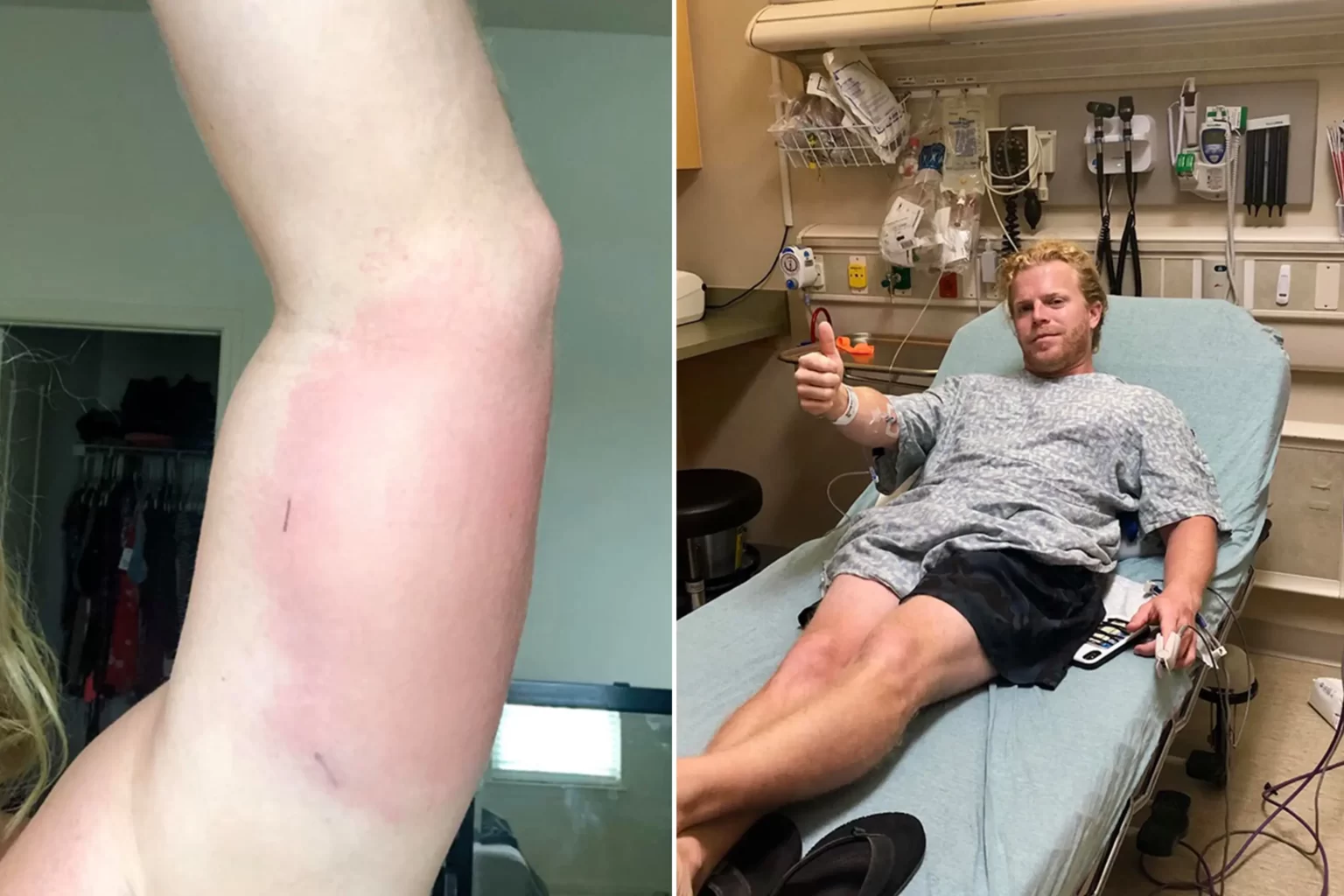
Flesh-eating bacteria, scientifically referred to as Necrotizing Fasciitis, is a rare but deadly bacterial infection that can swiftly devour skin, fat, and muscle tissues. While it is uncommon, the consequences can be catastrophic if not addressed promptly.
Causes and Sources
Warm Waters and Humidity
One of the primary reasons behind the prevalence of flesh-eating bacteria in Florida is the warm waters and high humidity. These conditions create an ideal breeding ground for these harmful bacteria.
Wound Exposure
Flesh-eating bacteria can enter the body through even minor wounds, cuts, or insect bites. The bacteria then spread rapidly, causing severe infections.
Symptoms to Watch Out For
Early Indicators
In the initial stages, the symptoms of a flesh-eating bacterial infection may resemble common skin problems, making early diagnosis challenging. These include redness, swelling, warmth, and pain in the affected area.
Rapid Progression
As the infection progresses, symptoms intensify, leading to severe pain, blistering, and the development of dark patches on the skin. It’s crucial to seek immediate medical attention if you notice these signs.
Preventive Measures
Beach Safety
When visiting Florida’s beautiful beaches, it’s essential to follow safety guidelines. Avoid swimming in open wounds, and ensure you have no open cuts or injuries when entering the water.
Proper Wound Care
Carefully clean and cover any cuts or scrapes to prevent bacterial entry. Quick action can make all the difference.
Treatment Options
Surgical Intervention
In severe cases, surgery is often necessary to remove the infected tissues. This procedure is essential to stop the rapid spread of the infection.
Antibiotics
Doctors prescribe antibiotics to fight the bacteria and prevent further complications. Timely intervention is crucial to saving lives.
Conclusion
Flesh-eating bacteria in Florida is a hidden danger that demands attention. While rare, the potential consequences are severe. Warm weather and humid conditions contribute to its prevalence, and early detection and treatment are essential. When enjoying the beauty of Florida, always prioritize safety and proper wound care to reduce your risk of encountering this menacing bacteria.
FAQs
1. How common is flesh-eating bacteria in Florida?
Flesh-eating bacteria is relatively rare, but the warm and humid climate of Florida can make it more prevalent, especially near coastal areas.
2. Are there any specific precautions I can take to avoid infection?
Yes, avoid swimming in open wounds, and always keep cuts and scrapes well-cleaned and covered when in Florida’s waters.
3. What are the chances of survival if someone contracts flesh-eating bacteria?
Survival rates improve significantly with early diagnosis and prompt medical intervention. It is crucial to seek medical attention as soon as you notice concerning symptoms.
4. Can you get flesh-eating bacteria from eating seafood in Florida?
No, you cannot get flesh-eating bacteria from consuming seafood. It is primarily a concern when open wounds come into contact with contaminated water.
5. Is it safe to enjoy Florida’s beaches despite the risk of flesh-eating bacteria?
Yes, it is safe to enjoy Florida’s beaches with proper precautions. Being aware of the risks and following safety guidelines can help reduce the chances of infection.