Tonsillar Hypertrophy: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Introduction
Tonsillar hypertrophy refers to the enlargement of the tonsils, which are two masses of tissue located at the back of the throat. This condition can affect individuals of all ages, but it is commonly seen in children. Tonsillar hypertrophy can lead to various uncomfortable symptoms and may require medical intervention. In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for tonsillar hypertrophy.
Understanding Tonsillar Hypertrophy
Tonsillar hypertrophy refers to the enlargement of the tonsils beyond their normal size. The tonsils are part of the lymphatic system and play a role in fighting infections. However, when they become enlarged, they can cause discomfort and interfere with normal bodily functions. Tonsillar hypertrophy can be unilateral (affecting only one tonsil) or bilateral (affecting both tonsils).
Causes of Tonsillar Hypertrophy
Several factors can contribute to tonsillar hypertrophy:
- Recurrent Infections: Chronic or recurrent tonsillitis, which is inflammation of the tonsils due to bacterial or viral infections, can lead to the enlargement of the tonsils.
- Allergies: Individuals with allergies may experience inflammation and swelling of the tonsils.
- Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA): Tonsillar hypertrophy can be associated with OSA, a condition characterized by breathing interruptions during sleep.
- Genetic Predisposition: Some individuals may have a genetic predisposition to developing tonsillar hypertrophy.
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to secondhand smoke or air pollution can contribute to the enlargement of the tonsils.
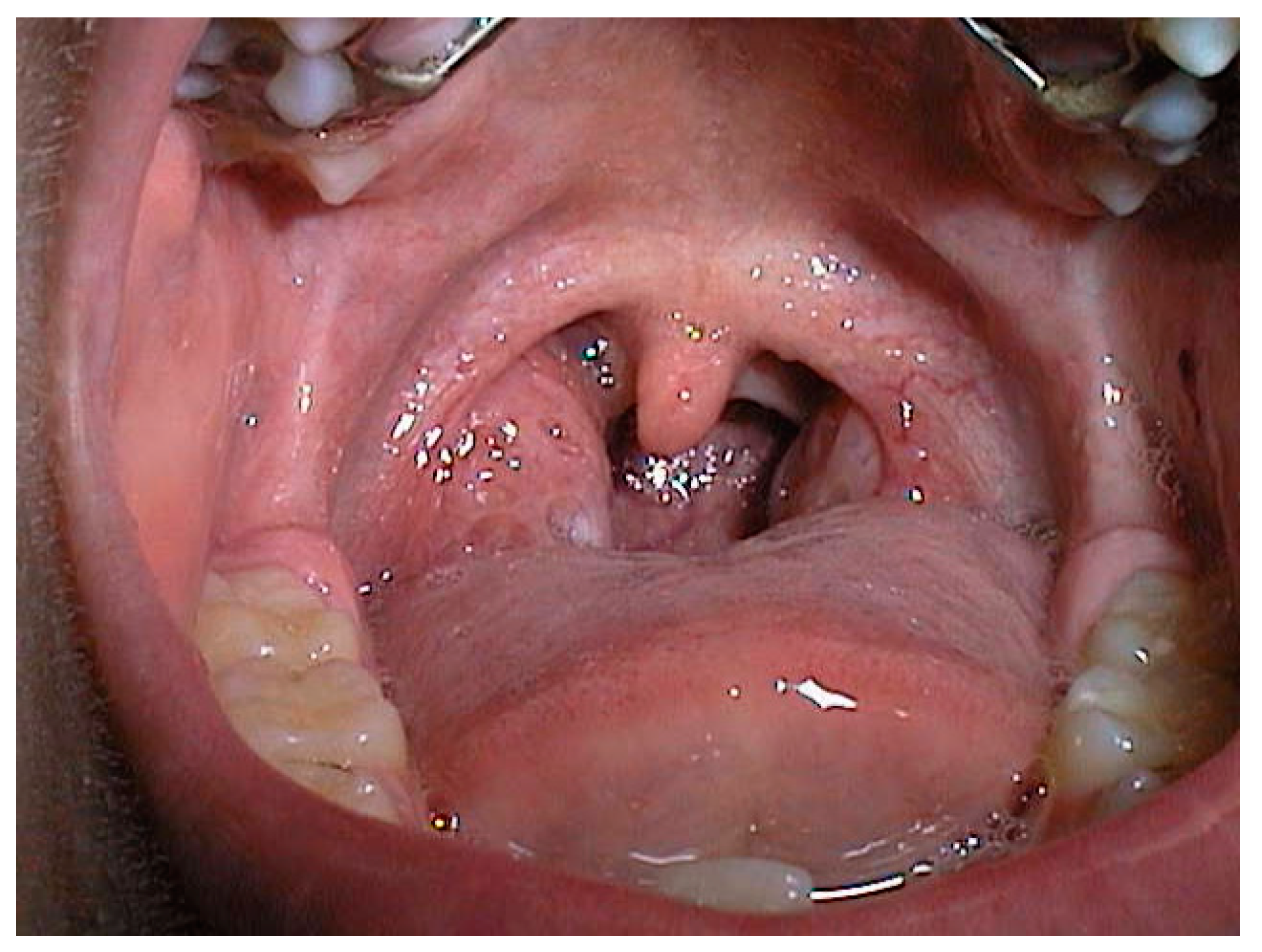
Common Symptoms
Tonsillar hypertrophy can cause a range of symptoms, including:
- Sore throat: Persistent or recurrent sore throat is a common symptom.
- Difficulty swallowing: Enlarged tonsils can make it difficult and painful to swallow food.
- Breathing difficulties: In severe cases, tonsillar hypertrophy can obstruct the airway, leading to breathing problems.
- Snoring: Enlarged tonsils can cause snoring, especially during sleep.
- Sleep disturbances: Sleep disruptions may occur due to breathing difficulties or sleep apnea.
- Tonsil stones: Enlarged tonsils can trap debris and bacteria, leading to the formation of small, hard masses called tonsil stones.
Diagnosis and Evaluation
If tonsillar hypertrophy is suspected, a medical professional will conduct a thorough evaluation. This may include:
- Medical History: The doctor will inquire about the patient’s symptoms, medical history, and any previous treatments.
- Physical Examination: A physical examination of the throat and neck will be performed to assess the size and condition of the tonsils.
- Additional Tests: In some cases, imaging tests, such as a throat X-ray or a CT scan, may be recommended to evaluate the severity of the condition.
Treatment Options
The treatment approach for tonsillar hypertrophy depends on the severity of the symptoms and the underlying cause. The following options may be considered:
Medications
- Pain relievers: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can help alleviate discomfort and reduce inflammation.
- Antibiotics: If the tonsillar hypertrophy is caused by a bacterial infection, antibiotics may be prescribed to eliminate the infection.
Lifestyle Changes
- Warm saltwater gargles: Gargling with warm saltwater can help reduce throat inflammation and alleviate discomfort.
- Hydration: Staying hydrated by drinking plenty of fluids can soothe the throat and promote healing.
Surgical Interventions
- Tonsillectomy: In cases of severe or recurrent tonsillar hypertrophy, a surgical procedure called tonsillectomy may be recommended. This involves the removal of the tonsils and is usually performed under general anesthesia.
- Adenotonsillectomy: If tonsillar hypertrophy is associated with obstructive sleep apnea, a combined surgery called adenotonsillectomy may be performed. This involves removing the tonsils and the adenoids, which are another set of lymphoid tissues located at the back of the nasal cavity.
Recovery and Aftercare
After a tonsillectomy or adenotonsillectomy, proper aftercare is essential for a smooth recovery. Some post-operative instructions may include:
- Pain management: The doctor may prescribe pain medication to manage any discomfort during the recovery period.
- Dietary adjustments: A soft or liquid diet may be recommended initially to avoid irritating the surgical site.
- Rest and recovery: Adequate rest and avoiding strenuous activities can promote healing and reduce the risk of complications.
- Follow-up appointments: Regular follow-up appointments will be scheduled to monitor the healing process and address any concerns.
Prevention Tips
While it may not be possible to prevent tonsillar hypertrophy entirely, the following tips can help reduce the risk or severity of the condition:
- Good hygiene practices: Encourage regular handwashing and avoid close contact with individuals who have respiratory infections.
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle: A balanced diet, regular exercise, and adequate sleep can help strengthen the immune system.
- Manage allergies: If allergies are a known trigger, seek appropriate medical treatment and avoid allergens whenever possible.
- Avoid secondhand smoke: Minimize exposure to secondhand smoke, as it can aggravate tonsillar inflammation.
Conclusion
Tonsillar hypertrophy is a condition characterized by the enlargement of the tonsils, which can lead to various uncomfortable symptoms. It can be caused by recurrent infections, allergies, or obstructive sleep apnea. Treatment options range from medications and lifestyle changes to surgical interventions such as tonsillectomy or adenotonsillectomy. If you experience persistent symptoms related to tonsillar hypertrophy, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
FAQs
1. Is tonsillar hypertrophy a serious condition? Tonsillar hypertrophy can cause significant discomfort and may interfere with normal bodily functions. While it is not always a serious condition, severe cases may require medical intervention.
2. Can tonsillar hypertrophy be treated with medications alone? In some cases, medications such as pain relievers or antibiotics can provide relief and resolve the underlying cause. However, surgical intervention may be necessary for severe or recurrent tonsillar hypertrophy.
3. How long does it take to recover from a tonsillectomy? Recovery time can vary depending on the individual, but it typically takes about 10 to 14 days to fully recover from a tonsillectomy.
4. Can tonsillar hypertrophy recur after surgical removal? While tonsillectomy is an effective treatment for tonsillar hypertrophy, there is a small possibility of regrowth. However, recurrent tonsillar hypertrophy is relatively rare.
5. Can tonsillar hypertrophy affect adults? Although tonsillar hypertrophy is commonly seen in children, it can also affect adults. The symptoms and treatment options are generally similar regardless of age.



